In the present article we perform a deep dive into a Mirai threat sample first seen in wild on today 28th March 2025.
Hashes: 67b9093116482df90590806ce4e460a5cb4d5a543b31bd77cd0162c6ef12b482
39804a46b96d367ed3347ca49d621089dd4ad07a
8a9bef3b034477a2a8918c294fdd1b98
Main points of the analysis:
- ELF botnet
- POST requests with SEFA useragent
- wget commands
- exploit commands and fake time setting
- C&C IP address and server
- iptables commands to drop TCP packets on port 5555
- sockets connections
- checksum of the sessions
- flooding and UDP flooding
- exploit scanner
- killer_pid and killer_path process parameters
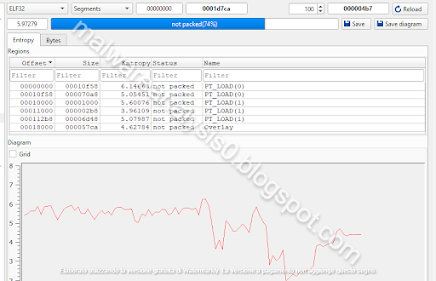
The artifact is a 32-Bit ELF file, here are some details about the sections:
The entropy is not so high and the sample is not packed:
Here are the details of the POST requests made with the useragent SEFA:
Based on "r0" variable value there is different system calls: Exit (__GI_exit) or __GI_sleep with the time of "arg1" value and kills the parent process with the process ID returned by getppid() function.
Here are some details of attack_kill_all() function which checks the ongoing status of the infection killchain and it can kills the processes responsible of the Botnet attack phase. If the "attack_ongoing_1" variable has the value 0 the data_212e0 value is checked and if it's different from zero the label label_8558 is called, otherwise the label label_8514 is called and if the data_212e4 is different from zero the processes are killed with __GI_kill system call.
The "atoi" function is used to convert r0_1 characters to integer values:
Before connecting to the socket some random data is added to "sa_data" array variable with "ro_17" variable.
Here we have the __GI_connect system call to the socket created and sending operations in while(true) loops:
We can see there are also checksum phases in the sessions of sockets connections and sending operations:
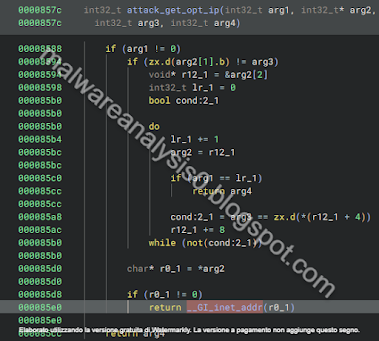
Here we can see the exploit_kill() function which kills the exploit process with the PID (obtained with the pointer data_9f64) and the exploit_setup_connection function with initialize and build the socket session for exploit phases:
After the closing of the socket session the "arg1" variable, which contains the result, the second cell is filled in with exploit_fake_time variable (got with the pointer to data_a038 variable).
Here we can see the editing and management of data buffers for exploit scanner raw packets, thanks also to randomized content in the variables "r0_15", "r0_16" and "r2_12".
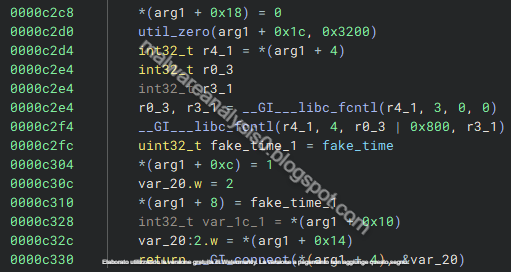
Here is the setup_connection function, also in this case a socket connection is created with exploit fake time parameter:
67b9093116482df90590806ce4e460a5cb4d5a543b31bd77cd0162c6ef12b482
39804a46b96d367ed3347ca49d621089dd4ad07a
8a9bef3b034477a2a8918c294fdd1b98
154.213.189[.]145
icy[.]sh
YARA rules:
rule Mirai28March2025
{
strings:
$str = "killer_realpath"
$hex = { 6b 69 6c 6c 65 72 5f 72 65 61 6c 70 61 74 68 }
condition:
$str or $hex
}
rule Mirai28March2025CnC {
meta:
description = "Detects Mirai with C&C information"
condition:
vt.net.url.raw icontains "154.213.189[.]145"
}